Intentar ORO - Gratis
Millet might
Down To Earth
|September 16, 2022
Odisha's mission to bring millets back to its fields and plates can succeed with greater marketing support and promotion beyond tribal areas

SUPPLY creates its own demand. This theory, believed to have been proposed by the early 19th-century French economist Jean-Baptiste Say, may sound like a foolhardy view to the modern ear, but this is how India lost the diversity of its food basket to Green Revolution. In the 1960s, as the country was struggling to feed itself, the focus was to rapidly increase the production of two crops-wheat and rice. This shaped an Indian diet where rice and wheat became the staple food, eventually reducing the demand for other traditional cereal grains like millets. Assessments in recent decades show that while the Green Revolution has not helped address the nutritional security of India, it has turned the country into the world's biggest extractor of groundwater. Heavy reliance on chemical inputs has degraded soil, polluted water sources and is harming farmers' health.
Fifty years later, as Odisha tries to improve nutritional security and promote sustainable agricultural practices, Say's law has come in handy. In 2017, the state launched the Odisha Millet Mission (OMM), which aims to bring millets back to its fields and food plates by encouraging farmers to grow the crops that traditionally formed a substantial part of the diet and crop system in tribal areas. This highly varied group of small-seeded cereal crops not only require less water, farm inputs and are more resilient to climate vulnerability, but rich in nutrients like calcium, iron and protein (see 'Better for the food plate').
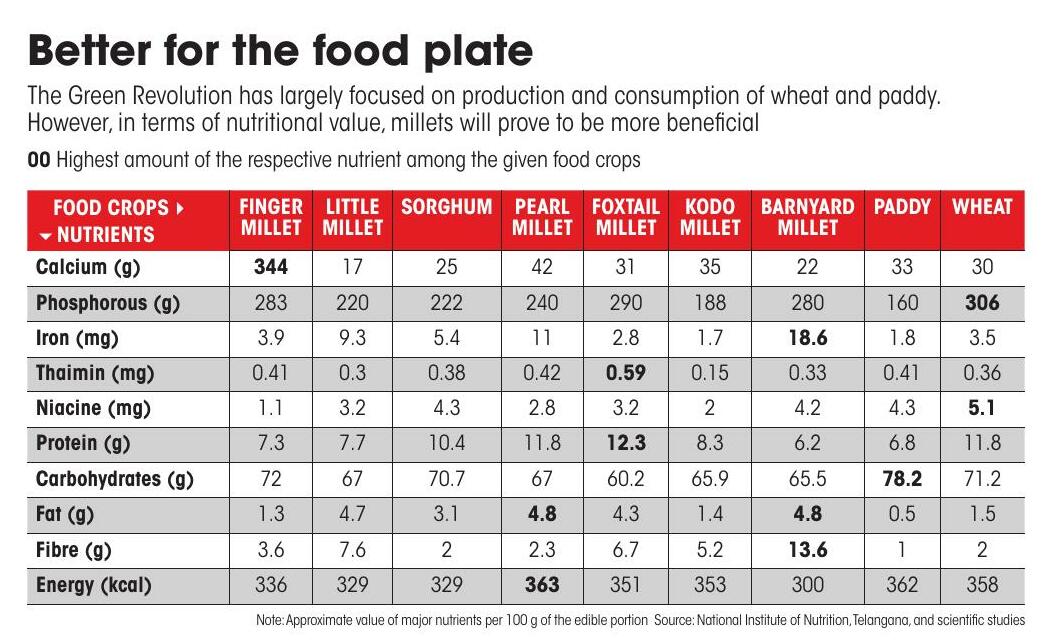
Esta historia es de la edición September 16, 2022 de Down To Earth.
Suscríbete a Magzter GOLD para acceder a miles de historias premium seleccionadas y a más de 9000 revistas y periódicos.
¿Ya eres suscriptor? Iniciar sesión
MÁS HISTORIAS DE Down To Earth

Down To Earth
THINK TWICE BEFORE FELLING SAL TREES
Many trees considered to be affected by sal borer in the 1990s are still alive today
1 mins
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
EDGE OF SURVIVAL
Caste divides deny marginalised communities land, resources and essential aid, leaving them more vulnerable to climate disasters
6 mins
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
A WISH LIST?
Union Budget for 2026-27 conveys the impression of a roll-call of intentions and ambitious proposals, with little detail on their formulation
6 mins
February 16, 2026
Down To Earth
Break down the gender wall
THE RULING National Democratic Alliance (NDA) government has been heavily invested in the goal to make India a developed economy by 2047.
2 mins
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
MENSTRUAL HEALTH, NOW A FUNDAMENTAL RIGHT
In a landmark judgement, the Supreme Court has recognised menstrual health and hygiene as a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution of India, which guarantees the right to life and dignity.
8 mins
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
Of devolution and new disasters
The 16th Finance Commission pushes for changes in view of new fiscal and climatic conditions
11 mins
February 16, 2026
Down To Earth
Rising risks of plastics
NEGATIVE IMPACTS on human health due to emissions linked to the plastic lifecycle could double by 2040, according to a study published in The Lancet Planetary Health in January.
1 min
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
GAP BETWEEN EPIDEMICS NARROWING
A watershed-based and landscape-level approach is needed to address forest degradation
2 mins
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
WAITING TO STRIKE
Sal heartwood borer is considered the biggest threat to forestry in India, especially to the sal tree, where it lives and breeds.
11 mins
February 16, 2026

Down To Earth
A SPRING DELIGHT
Mustard flowers are not meant only for the eyes. Invite them to your plate once in a while
3 mins
February 16, 2026
Translate
Change font size

