Intentar ORO - Gratis
DEAD LINES
Down To Earth
|June 16, 2020
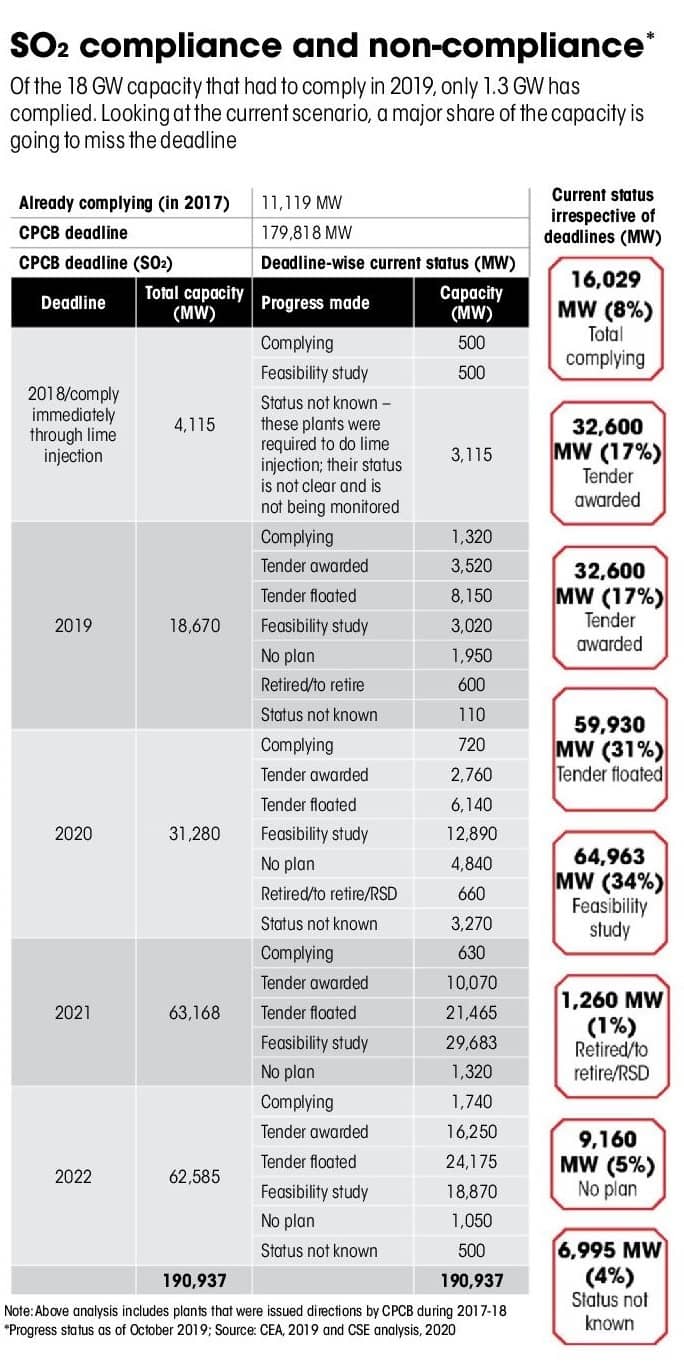
More than 70 per cent coal-fired power plants will not meet environmental norms by 2022, five years after their deadline was extended, says a new report by Delhi-based non-profit Centre for Science and Environment
-

COAL-FIRED thermal power plants (TPPs) generate about 56 per cent of the country’s energy needs. But they a resource-intensive and polluting industry— they account for over 60 per cent of industrial emissions of particulate matter (PM); 45 per cent of sulphur dioxide (SO 2); 30 per cent of oxides of nitrogen (NO x); and, over 80 per cent of mercury emissions. Moreover, the sector is responsible for 70 per cent of total freshwater withdrawals. A 2017 study by the US-based University of Maryland says that India will soon become the world’s top emitter of SO 2. This scenario has arisen due to lack of effective control measures over the decades in India.
In 2015, the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), a Delhi-based non-profit, recommended a revision of the sector’s emission norms. Taking cognisance, the Union ministry of environment, forest and climate change (MoEFCC) notified the new norms, and wanted them to be implemented by 2017. But the industry not only obstructed and prevaricated this move, but tried to use the Supreme Court and other agencies to shift the deadline from 2017 to 2024. Finally, the deadline was extended to 2022. But a new report by
CSE, Coal-based Power Norms: Where do we stand today, finds that with barely two years to go before the deadline hits them, almost 70 per cent of the plants will not meet the emission standards. Says CSE Director General Sunita Narain: “Our assessment finds that even after seven years since the notification and even after the agreed five-year extension given to this sector in 2017, most of the total installed coal-fired capacity will not be compliant with the crucial SO 2 standards by 2022” (see ‘SO 2 compliance and non-compliance’).
Esta historia es de la edición June 16, 2020 de Down To Earth.
Suscríbete a Magzter GOLD para acceder a miles de historias premium seleccionadas y a más de 9000 revistas y periódicos.
¿Ya eres suscriptor? Iniciar sesión
MÁS HISTORIAS DE Down To Earth
Down To Earth
Popular distrust
THE WORLD seems to be going through a period of stasis despite facing an unfathomable polycrisis.
2 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
CONSERVE OR PERISH
Periyar Tiger Reserve has rewritten Indian conservation by turning poachers into protectors and conflict into coexistence
5 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
'Rivers need to run free'
From Tibet to West Bengal, the Brahmaputra is the pulse of communities and ecosystems along its course. But what are the risks the river faces through human interventions, particularly dams, discusses journalist, author and filmmaker SANJOY HAZARIKA in his new book, River Traveller.
4 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
India is facing up to its innovation lag
There are signs now that India is acknowledging the superior strides made by China in a frontier technology like Al
4 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
Competing concerns
What are the repercussions of the EU-Mercosur pact that have made European farmers protest against the free trade agreement?
4 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
From fryer to flight
Sustainable fuel made from used cooking oil can play a pivotal role in helping India achieve its aviation emission reduction goals. Measures to collect this oil must be revamped
4 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
ACCESS OPEN
An amendment to India's nodal forest conservation law opens up forests across India to commercial exploitation by the paper industry
6 mins
February 01, 2026
Down To Earth
DRINK FROM TAP CAN BE A REALITY
As cities across India struggle to supply safe piped water, Odisha offers a success story
2 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
GREAT DRYING
The Earth is hotter than at any point in the past 100,000 years, with 2023-25 becoming the warmest three-year period on record and also breaching the 1.5°C threshold for the first time. One fallout is dwindling freshwater.
22 mins
February 01, 2026

Down To Earth
Green redemption
Restoration of grasslands of Kerala's Pampadum Shola National Park, once dominated by invasive Australian wattles, see a return of streams and native species
1 mins
February 01, 2026
Translate
Change font size
