Poging GOUD - Vrij
Betelgeuse's spectacular blow-out
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
|October 2022
A mass ejection larger than the Moon caused the star's dimming in 2019
-
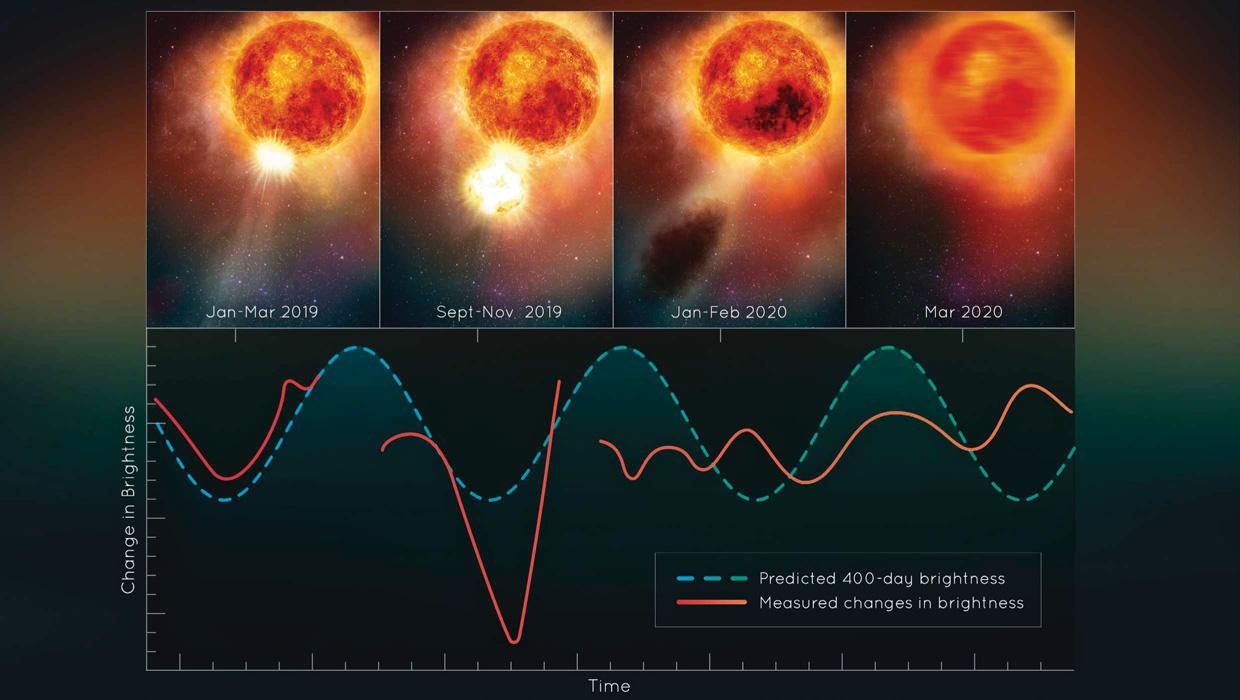
Three years ago, amateur astronomers around the world watched as the usually bright light of Betelgeuse dimmed overnight and remained that way for several months. Now a group of astronomers have determined it was caused by a piece of the star's atmosphere being ejected into space.
"We've never before seen a huge mass ejection of the surface of a star," says Andrea Dupree from the Center for Astrophysics, Harvard and Smithsonian, who led the study.
Betelgeuse is a red giant star over 1.6 billion kilometres wide - meaning if it replaced our Sun it would swamp Jupiter and almost reach Saturn. It has ballooned in size as it is approaching the end of its life and will eventually go supernova.
Though this is unlikely to happen for the next 10,000 years, it gives astronomers a unique view of a star in its final centuries. Over 200 years of observations have shown that the star's brightness slowly pulses according to a 400-day cycle, but the scale and speed of the 2019 dimming was unprecedented.
Drawing together observations from all over the world, Dupree has determined that material bubbling up within the star blasted off a piece of the photosphere. The ejection had a mass several times that of our Moon - a colossal 400 billion times more than what our Sun typically gives off during coronal mass ejections. As this fractured piece cooled, it formed a dust cloud that blocked Betelgeuse's light from Earth, causing it to appear dimmer.
It also appears that Betelgeuse's 400-day brightness cycle has stopped, or at least paused. Spectral Hubble observations taken by Dupree showed signs that this event and the star's attempts to rebuild its photosphere have disrupted the internal motions that drive the cycle.
Dit verhaal komt uit de October 2022-editie van BBC Sky at Night Magazine.
Abonneer u op Magzter GOLD voor toegang tot duizenden zorgvuldig samengestelde premiumverhalen en meer dan 9000 tijdschriften en kranten.
Bent u al abonnee? Aanmelden
MEER VERHALEN VAN BBC Sky at Night Magazine
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
The Giant Leap: Why Space is the Next Frontier in the Evolution of Life
“Earth is the cradle of humanity, but one cannot live in the cradle forever,” wrote Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in 1911.
1 mins
February 2026

BBC Sky at Night Magazine
Tele Vue Nagler Type-7 series eyepieces
These premium optics were inspired by Apollo - and deliver a giant leap to your views
4 mins
February 2026
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
Once Upon a Time in Space
While the Space Race of the Cold War years was ultimately a geopolitical contest between the USA and the Soviet Union, the rivalry sparked rapid innovation and inspired multiple generations to look skyward.
1 mins
February 2026
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
The Multiverse: When One Universe Isn't Enough
The concept of a 'multiverse' – the idea that our Universe may be just one of many – is widespread in science fiction and a common thread of online discussions.
1 mins
February 2026

BBC Sky at Night Magazine
Q&A WITH A GAMMA RAY SPECIALIST
In 2025, astronomers detected a blast from space that lasted seven hours. Now they're uncovering the strange processes behind the exceptional outburst
3 mins
February 2026

BBC Sky at Night Magazine
Astronomy Photographer of the Year
The world-leading astrophotography competition returns. Could your image take the top prize of £10,000?
2 mins
February 2026
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
MOONWATCH
February's top lunar feature to observe
2 mins
February 2026

BBC Sky at Night Magazine
NOVAStar Scarlet A62Q 62mm f/8.4 quadruplet achromatic refractor
Well-built and capable, this beginner scope punches well above its bargain price
4 mins
February 2026
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
STAR OF THE MONTH
Rasalas, Leo the Lion's metal-rich crown
1 min
February 2026
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
Comet 24P/Schaumasse
Having reached perihelion on 8 January, comet 24P/ Schaumasse is now fading. Starting the month at a small-telescope-friendly mag. +10.5, it dims throughout February to below 12th magnitude.
1 min
February 2026
Translate
Change font size

