Prøve GULL - Gratis
This Is the Closest Scientists Have Gotten to Reaching Absolute Zero
Popular Mechanics
|March - April 2022
The absolute temperature scale gives measurements in Kelvins-unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit, which use degrees. Absolute zero is thus 0 Kelvin, not 0 degrees Kelvin.
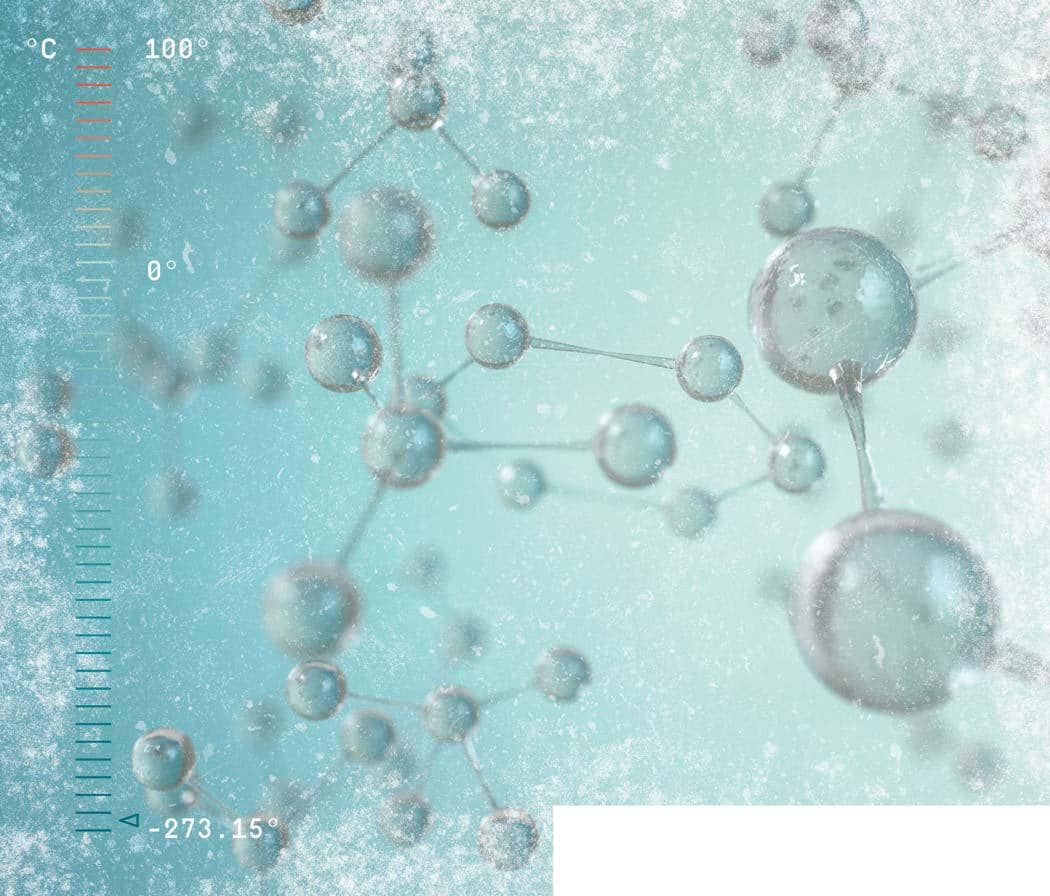
RESEARCHERS FROM FOUR UNIVERSITIES in Germany have conditioned a lab to register the coldest effective temperature in a research-controlled environment ever recorded-38 trillionths of a Kelvin above absolute zero. According to a 2021 study published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the temperature persisted for two seconds at the University of Bremen's Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity (ZARM), and the conditions that made this possible could have longstanding ramifications for quantum mechanics.
Absolute zero is 0 Kelvin, equal to -273.15 degrees Celsius, or -459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. This is the point at which particles are essentially motionless, and it's the lowest possible temperature we could ever theoretically reach, according to the laws of thermodynamics. Some researchers seek absolute zero for use in precision instruments that can test the fundamental laws of physics, while others do so to model something called the Cold Big Bang, when all matter exploded into being and the universe began operating under observable laws of matter and energy. In this latter sense, looking at a system at absolute zero-one almost completely without kinetic energy-would be close to observing the very beginning of physics.
Denne historien er fra March - April 2022-utgaven av Popular Mechanics.
Abonner på Magzter GOLD for å få tilgang til tusenvis av kuraterte premiumhistorier og over 9000 magasiner og aviser.
Allerede abonnent? Logg på
FLERE HISTORIER FRA Popular Mechanics

Popular Mechanics US
HOW TO UNCLOG A SINK
IF YOUR SINK IS CLOGGED AND PLUNGING fails to clear the blockage, look to your P-trap (or simply, “trap”) before calling a plumber.
1 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
A WEIRD (AND FREE!) SOUND SYSTEM HACK
THERE ARE SO MANY VARIABLES TO how a room's dimensions, a building's construction, the placement of furniture, and the materials of that furniture affect the sound of speakers and subwoofers that there's no way to offer a one-size-fits-all, \"put it here\" maxim for the absolute best subwoofer sound quality.
1 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
The Fringes of Life
AT FIRST GLANCE, CREATING A DEFINItion of \"life\" seems simple.
2 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
THE SAND THIEVES
Sand is the hidden architecture of our modern world—but it's running out. Global mafias are stealing this precious resource from right beneath our feet, and they're willing to kill for it.
18 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
OPERATION PLUTO
THE ALLIES’ SECRET UNDERWATER WEAPON THAT HELPED DEFEAT THE NAZIS
13 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
5 WAYS TO KEEP YOUR GENERATOR IN WORKING ORDER
IF YOU HAVE A GAS GENERAtor, use ethanol-free gas treated with fuel stabilizer, and maintain a full tank when not in use; keep a gas can full of stabilized fuel on hand during peak disaster season.
1 min
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
Minivans
MINIVANS ARE MAKING A COMEBACK, and that's kind of surprising, as they're some of the most polarizing vehicles on the road and have always been built with a function-over-form ethos.
1 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
3 WAYS TO FIND A STUD WITHOUT A STUD FINDER
There is a noticeably hollow sound when you knock on the space between the studs versus when you knock on drywall that has a stud behind it.
1 min
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
A Cell-Sized Elephant
EVER SINCE THE POPULARITY OF 3D printing skyrocketed in the midaughts, people have been manufacturing everything from chocolate to rocket fuel-and that list now includes a microscopic elephant inside of a living cell. Technology has really leveled up since 2005.
1 mins
January / February 2026

Popular Mechanics US
WHO SETS THE DOOMSDAY CLOCK?
In the shadow of my family's atomic legacy, I set out to understand the increasingly urgent debate about humanity's capacity to end itself and what it can teach us about living.
21 mins
January / February 2026
Translate
Change font size
