A spectacular villa under Positano sees the light.

Once we reach the spot, you The eruption of won’t believe your eyes,” says Mount Vesuvius archaeologist Luciana Jacobelli in A.D.. 79 buried not only the towns of the University of Molise as she of Pompeii and opens a small door to the crypt Herculaneum, but of the church of Santa Maria also a number Assunta in the center of town. It’s very dim inside, of seaside villas and she has to use a flashlight as we make our way. along the Amalfi Coast. Below, a We slowly climb down a series of ladders through fragment of the a forest of iron scaffolding toward what seems to Positano villa’s be the only well-lit area, nearly 30 feet under the vibrant fresco wall church. Jacobelli then leads me into a room and, as painting. promised, frescoes in dazzling green, yellow, red, and blue seem to illuminate the space on their own. We have arrived at the extraordinarily well-preserved remains of a lavish villa marittima, or seaside villa, once a luxurious retreat for the rich of ancient Rome to escape the summer heat and the hustle and bustle of city life in the first centuries B.C. and A.D.
この記事は Archaeology の September/October 2016 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、8,500 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です ? サインイン
この記事は Archaeology の September/October 2016 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、8,500 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です? サインイン
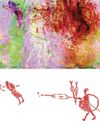
A Very Close Encounter
New research has shown that human figures painted in red on a rock art panel in central Montana depict individuals engaged in a life-or-death encounter during an especially fraught historical moment.

A Sword for the Ages
A zigzag pattern, now tinged with the green-blue patina of oxidized metal, adorns the octagonal hilt of a rare sword dating to the Middle Bronze Age in Germany (1600-1200 B.C.) that was recently excavated in the Bavarian town of Nördlingen.

Ancient Egyptian Astrology
For centuries, layers of soot have coated the ceilings and columns in the entrance hall of Egypt's Temple of Esna. Now, an Egyptian-German team of researchers, led by Hisham El-Leithy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities and Christian Leitz of the University of Tübingen, is restoring the temple's vibrant painted reliefs to their original brilliance.

BRONZE AGE POWER PLAYERS
How Hittite kings forged diplomatic ties with a shadowy Greek city-state

RITES OF REBELLION
Archaeologists unearth evidence of a 500-year-old resistance movement high in the Andes

Secrets of Egypt's Golden Boy
CT scans offer researchers a virtual look deep inside a mummy's coffin

When Lions Were King
Across the ancient world, people adopted the big cats as sacred symbols of power and protection

UKRAINE'S LOST CAPITAL
In 1708, Peter the Great destroyed Baturyn, a bastion of Cossack independence and culture

LAPAKAHI VILLAGE, HAWAII
Standing beside a cove on the northwest coast of the island of Hawaii, the fishing village of Lapakahi, which is surrounded by black lava stone walls, was once home to generations of fishers and farmers known throughout the archipelago for their mastery of la'au lapa'au, or the practice of traditional Hawaiian medicine. \"

A MORE COMFORTABLE RIDE
Although the date is much debated, most scholars believe people 5,000 years ago. For thousands of years after that, they did so without saddles. \"In comparison with horse riding, the development of saddles began relatively late, when riders began to care more about comfort and safety in addition to the horse's health,\" says University of Zurich archaeologist Patrick Wertmann.