Spectacular new discoveries from the Caucasus set the stage for a dramatic hilltop ritual.

RUSSIAN ARCHAEOLOGIST ANDREY BELINSKI wasn’t sure what to expect when he found himself facing a small mound in a farmer’s field at the foot of the Caucasus Mountains. To the untrained eye, the 12-foot feature looked like little more than a hillock. To Belinski, who was charged with excavating the area to make way for new power lines, it looked like a type of ancient burial mound called a kurgan. He considered the job of excavating and analyzing the kurgan, which might be damaged by the construction work, fairly routine. “Basically, we planned to dig so we could understand how it was built,” Belinski says. As he and his team began to slice into the mound, located 30 miles east of Stavropol, it became apparent that they weren’t the first people to take an interest. In fact, looters had long ago ravaged some sections. “The central part was destroyed, probably in the nineteenth century,” Belinski says. Hopes of finding a burial chamber or artifacts inside began to fade.
It took nearly a month of digging to reach the bottom. There, Belinski ran into a layer of thick clay that, at first glance, looked like a natural feature of the landscape, not the result of human activity. He uncovered a stone box, a foot or so deep, containing a few finger and rib bones from a teenager. But that wasn’t all. Nested one inside the other in the box were two gold vessels of unsurpassed workmanship. Beneath these lay three gold armbands, a heavy ring, and three smaller bell-shaped gold cups. “It was a huge surprise for us,” Belinski says. “Somehow, the people who plundered the rest didn’t locate these artifacts.”
この記事は Archaeology の July/August 2016 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、8,500 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です ? サインイン
この記事は Archaeology の July/August 2016 版に掲載されています。
7 日間の Magzter GOLD 無料トライアルを開始して、何千もの厳選されたプレミアム ストーリー、8,500 以上の雑誌や新聞にアクセスしてください。
すでに購読者です? サインイン
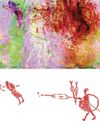
A Very Close Encounter
New research has shown that human figures painted in red on a rock art panel in central Montana depict individuals engaged in a life-or-death encounter during an especially fraught historical moment.

A Sword for the Ages
A zigzag pattern, now tinged with the green-blue patina of oxidized metal, adorns the octagonal hilt of a rare sword dating to the Middle Bronze Age in Germany (1600-1200 B.C.) that was recently excavated in the Bavarian town of Nördlingen.

Ancient Egyptian Astrology
For centuries, layers of soot have coated the ceilings and columns in the entrance hall of Egypt's Temple of Esna. Now, an Egyptian-German team of researchers, led by Hisham El-Leithy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities and Christian Leitz of the University of Tübingen, is restoring the temple's vibrant painted reliefs to their original brilliance.

BRONZE AGE POWER PLAYERS
How Hittite kings forged diplomatic ties with a shadowy Greek city-state

RITES OF REBELLION
Archaeologists unearth evidence of a 500-year-old resistance movement high in the Andes

Secrets of Egypt's Golden Boy
CT scans offer researchers a virtual look deep inside a mummy's coffin

When Lions Were King
Across the ancient world, people adopted the big cats as sacred symbols of power and protection

UKRAINE'S LOST CAPITAL
In 1708, Peter the Great destroyed Baturyn, a bastion of Cossack independence and culture

LAPAKAHI VILLAGE, HAWAII
Standing beside a cove on the northwest coast of the island of Hawaii, the fishing village of Lapakahi, which is surrounded by black lava stone walls, was once home to generations of fishers and farmers known throughout the archipelago for their mastery of la'au lapa'au, or the practice of traditional Hawaiian medicine. \"

A MORE COMFORTABLE RIDE
Although the date is much debated, most scholars believe people 5,000 years ago. For thousands of years after that, they did so without saddles. \"In comparison with horse riding, the development of saddles began relatively late, when riders began to care more about comfort and safety in addition to the horse's health,\" says University of Zurich archaeologist Patrick Wertmann.