
WHEN ARCHAEOLOGIST Brian Hayden of Simon Fraser University started working at the Keatley Creek site in British Columbia more than three decades ago, he was intrigued by nine small structures that had been clearly set apart from the main settlement. Located on a terrace above the Fraser River Gorge in the traditional territory of the Ts’kw’aylaxw (pronounced Tskwai-lah) First Nation, Keatley Creek was once one of the largest prehistoric settlements in what is now Canada. As many as 1,000 residents, who survived by hunting, gathering, and fishing, lived there at its peak around 1,000 to 2,000 years ago. Millennia of occupation left behind more than 115 depressions in the main settlement, evidence of partially underground wooden dwellings called pit houses that were inhabited in the winter.
The nine structures that caught Hayden’s attention were 300 to 600 feet away from the main group. Unlike the other dwellings at the site, they had rock-lined hearths and yielded rare artifacts including gaming pieces and shells from the Pacific coast. They also were near large roasting pits measuring up to 30 feet in diameter that suggested feasting had once taken place there. After many years of research, Hayden now believes that some of these distinctive buildings were used by members of secret societies to hold ceremonies with the ultimate goal of gaining influence over their fellow villagers.
This story is from the July/August 2020 edition of Archaeology.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 8,500+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber ? Sign In
This story is from the July/August 2020 edition of Archaeology.
Start your 7-day Magzter GOLD free trial to access thousands of curated premium stories, and 8,500+ magazines and newspapers.
Already a subscriber? Sign In
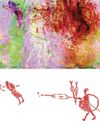
A Very Close Encounter
New research has shown that human figures painted in red on a rock art panel in central Montana depict individuals engaged in a life-or-death encounter during an especially fraught historical moment.

A Sword for the Ages
A zigzag pattern, now tinged with the green-blue patina of oxidized metal, adorns the octagonal hilt of a rare sword dating to the Middle Bronze Age in Germany (1600-1200 B.C.) that was recently excavated in the Bavarian town of Nördlingen.

Ancient Egyptian Astrology
For centuries, layers of soot have coated the ceilings and columns in the entrance hall of Egypt's Temple of Esna. Now, an Egyptian-German team of researchers, led by Hisham El-Leithy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities and Christian Leitz of the University of Tübingen, is restoring the temple's vibrant painted reliefs to their original brilliance.

BRONZE AGE POWER PLAYERS
How Hittite kings forged diplomatic ties with a shadowy Greek city-state

RITES OF REBELLION
Archaeologists unearth evidence of a 500-year-old resistance movement high in the Andes

Secrets of Egypt's Golden Boy
CT scans offer researchers a virtual look deep inside a mummy's coffin

When Lions Were King
Across the ancient world, people adopted the big cats as sacred symbols of power and protection

UKRAINE'S LOST CAPITAL
In 1708, Peter the Great destroyed Baturyn, a bastion of Cossack independence and culture

LAPAKAHI VILLAGE, HAWAII
Standing beside a cove on the northwest coast of the island of Hawaii, the fishing village of Lapakahi, which is surrounded by black lava stone walls, was once home to generations of fishers and farmers known throughout the archipelago for their mastery of la'au lapa'au, or the practice of traditional Hawaiian medicine. \"

A MORE COMFORTABLE RIDE
Although the date is much debated, most scholars believe people 5,000 years ago. For thousands of years after that, they did so without saddles. \"In comparison with horse riding, the development of saddles began relatively late, when riders began to care more about comfort and safety in addition to the horse's health,\" says University of Zurich archaeologist Patrick Wertmann.